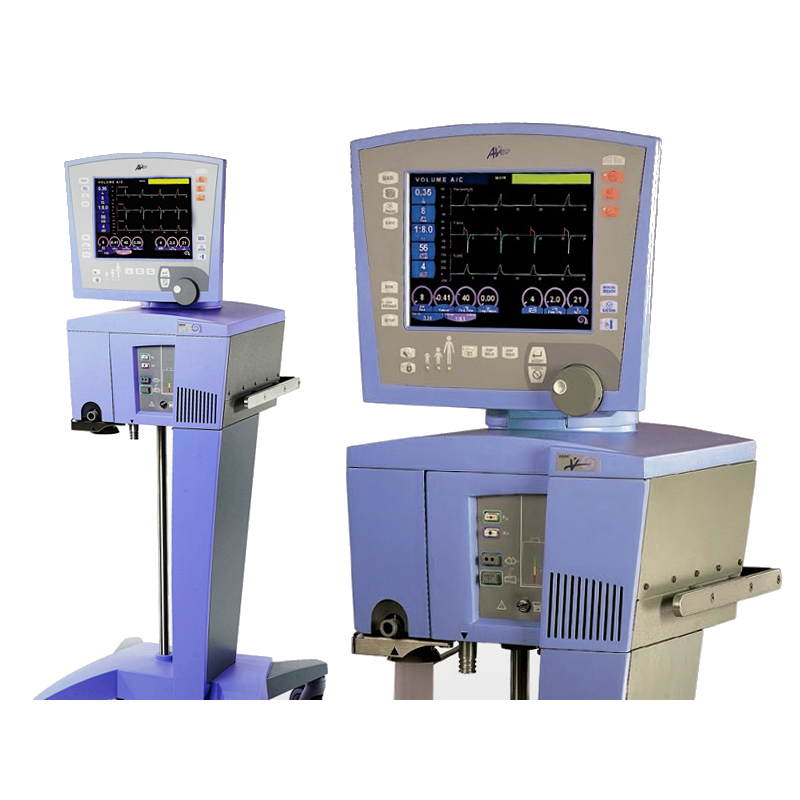
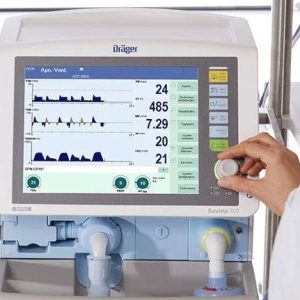
Avea Ventilator
Certified Refurbished Medical Equipment!
Vyaire CareFusion Avea Features
The Vyaire Carefusion Avea Ventilator can provide a wide range of ventilation modes with clinical tools and advanced monitoring. The Vyaire CareFusion Avea can offer critical care ventilation in both non-invasive and invasive ventilation modes for neonate, pediatric and adult patients. Some advanced tools include; BiCore Pulmonary monitoring, Heliox administration, and Volumetric Capnography. The Ventilator runs off of a Servo-controlled, software-driven ventilation system. as well as a user interface module that can maximize the flexibility of the ventilation to fit each patient’s needs. The front panel has a larger LCD touch screen making it easy to see the parameters being monitored while still being able to easily make changes. Another Vyaire Ventilator is the Vyaire Avea CVS.
$3,500.00
Vyaire CareFusion Avea Features
The Vyaire Carefusion Avea Ventilator can provide a wide range of ventilation modes with clinical tools and advanced monitoring. The Vyaire CareFusion Avea can offer critical care ventilation in both non-invasive and invasive ventilation modes for neonate, pediatric and adult patients. Some advanced tools include; BiCore Pulmonary monitoring, Heliox administration, and Volumetric Capnography. The Ventilator runs off of a Servo-controlled, software-driven ventilation system. as well as a user interface module that can maximize the flexibility of the ventilation to fit each patient’s needs. The front panel has a larger LCD touch screen making it easy to see the parameters being monitored while still being able to easily make changes. Another Vyaire Ventilator is the Vyaire Avea CVS.
This ventilator offers precision gas delivery system supplies accurate volumes.
Active exhalation valve on the CareFusion Avea promotes ventilator synchrony and comfort for your patients.
Volumetric Capnography gives clinicians more accurate tools to aid in quicker reaction during critical situations.
Accurate esophageal pressure measurements.
The AVEA provides a comprehensive array of modes and advanced features that keep you focused on your patient, not the equipment:
Volumetric capnography—Equipped with this option, this ventilator adds another key piece of information to provide improved monitoring of the patient’s condition. When tied with exclusive BiCore technology, this powerful tool provides the most comprehensive monitoring array of any ventilator available.
Precision gas delivery system—Supplied accurate tidal volumes from 2 mL to 2.5 L and was the first of its kind to compensate for heliox gas delivery automatically.
On-board compressor—The optional onboard air compressor can meet your patient’s needs whether in the intensive care unit (ICU) or moving to computerized tomography (CT) scan. This powerful scroll compressor can only be found on the ventilator and is capable of operating the ventilator for up to two hours on battery.*
Communication—Three different serial protocols can be selected from the utility screen to simplify integration with hospital information systems or remote alarm monitoring.
Vyaire CareFusion Avea Specifications
Dimensions
Pneumatic Module: 10.5” h x 16.75” w x 16” d (26.7 cm x 43.2 cm x 40.6 cm)
User interface Module: 13.75” h x 16.25” w x 2.5” d (35 cm x 41.3 cm x 6.4 cm)
Viewable Size: 12.1” (diagonal)
Resolution: 800 x 600
Weight
Ventilator w/ UIM no Compressor: < 73 lbs. (33.1 kg) Ventilator w/UIM and Compressor < 80 lbs (36.3 kg) Battery 1 hr of ventilator use on internal battery (standard) or 30 minutes ventilator and compressor. 4 hr of ventilator use on external battery or 2 hr ventilator and compressor. Setup Humidifier: Active and passive humidification Circuit compliance compensation: 0.0 to 7.5 mL/cmH2O Leak compensation: ON, OFF Endotracheal Tube Setup Diameter: 2.0 to 10.0 mm Length: 2.0 to 30.0 cm Automatic tube compensation: ON, OFF Patient Setup Patient weight: 0.1 to 300 kg Patient ID: Alphanumeric 24 characters Modes Mode type: A/C, SIMV, CPAP/PSV, NPPV, nasal CPAP/IMV Breath type: APRV/BiPhasic, Volume, Pressure, TCPL, PRVC, Volume Guarantee Apnea backup: Volume, pressure Primary Settings Rate: 1 to 150 bpm (neonatal, pediatric), 1 to 120 bpm (adult) Tidal volume: 2.0 mL to 2.5 L Inspiratory pressure: 0 to 80 cmH2O (neonatal), 0 to 90 cmH2O (adult, pediatric) Peak flow: 0.4 to 150 L/min Inspiratory time: 0.15 to 5.0 sec Pressure support ventilation: 0 to 80 cmH2O (neonatal), 0 to 90 cmH2O (adult, pediatric) PEEP: 0 to 50 cmH2O Flow trigger: 0.1 to 20 L/min %O2: 21% to 100% Pressure high (in APRV mode): 0 to 90 cmH2O Time high (in APRV mode): 0.2 to 30 sec Time low (in APRV mode): 0.2 to 30 sec Pressure low (in APRV mode): 0 to 45 cmH2O Advanced Settings Bias flow: 0.4 to 5.0 L/min Volume limit: 2.0 mL to 2.5 L Inspiratory rise: 1 to 9 Flow cycle: Off to 45% PSV rise: 1 to 9 PSV cycle: 5% to 45% PSV Tmax: 0.15 to 5.0 sec Waveform: Decelerating, square Sigh: ON, OFF Pressure trigger: 0.1 to 20 cmH2O Demand flow: ON, OFF Volumetric capnography: EtCO2 averaging 1 or 8 breaths, VCO2 averaging 3, 6, 9 or 12 minutes. Manual Controls Manual breath: One breath Expiratory hold: Maximum 20 sec (adult, pediatric), 3 sec (neonatal) Inspiratory hold: Maximum 3 seconds Increase O2: Set percentage O2 + 0% to 79% O2 Synchronized nebulizer: Available when peak flow > 15 L/min
Disconnect for suction: Active
Advanced Gas Blending System
Air/oxygen Blending: 21–100%
Internal Heliox Blending System: All concentrations from 80/20 helium/oxygen to 0/100 helium/oxygen
Advanced Patient Monitoring
Proximal hot wire flow sensor
Proximal variable orifice flow sensor (infant, pediatric, adult)
Proximal airway pressure monitoring
Tracheal pressure monitoring
Esophageal pressure monitoring
Volumetric capnography
Maneuvers
AutoPEEP Airway: 0–50 cmH2O (automated)
MIP/P100: -60 to 120 cmH2O (automated)
low Flow (Pflex): Automated
Alarms
Vent inop Ventilator inoperative
Loss of gas All gas sources lost
Circuit disconnect Patient circuit disconnected
Ext. high Ppeak High Ppeak longer than 5 seconds
Safety valve Safety valve open
Circuit occlusion Circuit occlusion
High Ppeak High peak pressure
Apnea interval Apnea interval exceeded
Loss of O2 Oxygen supply lost
Loss of air Air supply lost
Loss of heliox Heliox supply lost
Low battery Internal/external batteries low
Loss of A/C Main AC power lost
Low PEEP Low PEEP cmH2O
Low Ppeak Low PIP cmH2O
Low Vte Low tidal volume
Low Ve Low minute volume
Low %O2 Low FiO2 reading
High %O2 High FiO2 reading
ILV disconnect Independent lung ventilation lost
Alarm test Test alarm/set loudness
Invalid gas ID Gas type ID bad or missing
High Ve High minute volume
High rate High breath rate
Max insp time Inspiratory time limit exceeded
I:E limit I:E ratio limit exceeded
Fan failure Cooling fan failure
High Vt High tidal volume
Vol limit Volume limit exceeded
Low EtCO 3 2 Low end-tidal CO2
High EtCO 3 2 High end-tidal CO2
nCPAP pressure limit nCPAP pressure limit exceeded
Low nCPAP pressure Low nCPAP cmH2O
High nCPAP pressure High nCPAP cmH2O